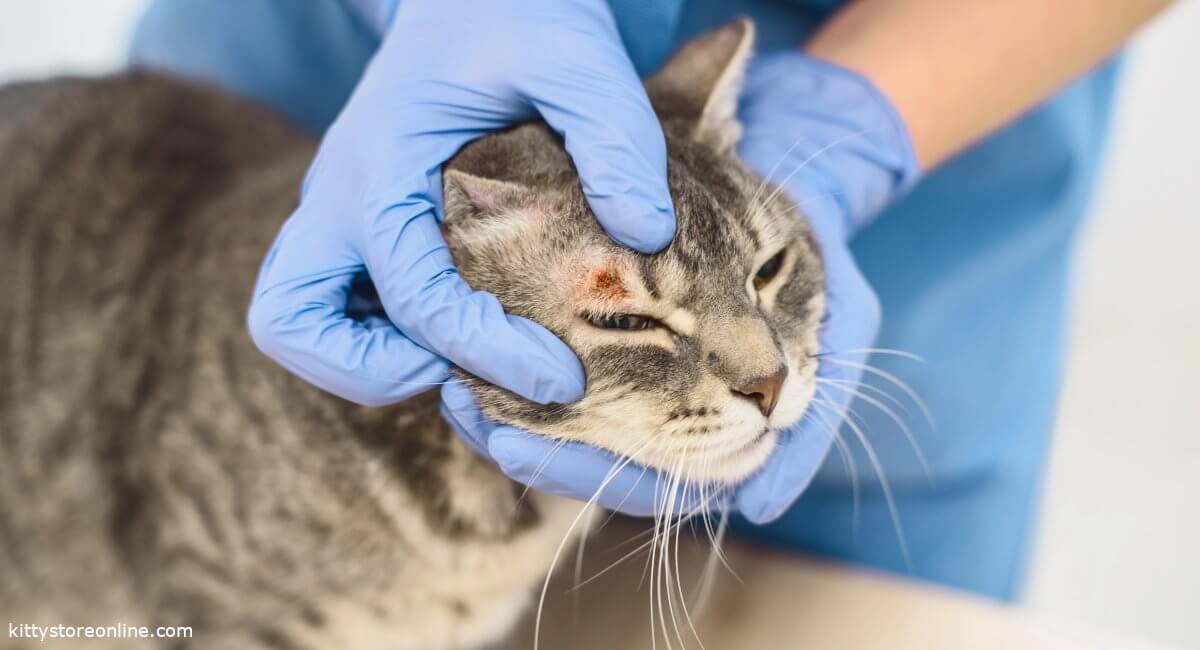
Fungal infection in cats is a serious health problem that affects many cat owners. The disease is often caused by skin fungi such as dermatophytosis. It can be contagious to both the affected cat and other pets. Humans can also become infected.
What does a fungal infection in cats mean?
A fungal infection is a disease caused by various types of fungi. The skin fungus Microsporum canis, which belongs to the so-called dermatophytes, is particularly common. These fungal infections mainly affect the cat’s skin, coat and sometimes also the claws. Bald patches in the coat, often accompanied by dandruff or redness, are particularly noticeable. Cats of any breed and any age can be affected. However, kittens, older cats or those with a weakened immune system are particularly susceptible. Fungal infections can have serious consequences if left untreated, which is why early diagnosis is crucial.
Causes and risk factors
The causes of a fungal infection in cats are varied. Infection often occurs through direct contact with an infected animal or a contaminated environment. Fungal spores can survive for weeks in textiles, carpets or scratching posts and thus represent a source of infection, while a weakened immune system significantly increases the risk of infection. Stress, poor hygiene and a cramped living environment can also have a favorable effect. Long-haired cats are particularly prone to developing a fungal disease due to their thick fur.
How do cats get a fungal infection?
Cats usually become infected through contact with other infected animals or contaminated objects. Animal shelters or street animals are also common sources of infection.
Are certain cat breeds more susceptible to fungal infections?
Long-haired breeds such as Persian cats are more susceptible, as the dense coat provides ideal conditions for fungi.
Can poor hygiene promote fungal infections in cats?
Yes, inadequate hygiene promotes the spread of fungal spores and increases the risk of infection.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Symptoms of a fungal infection
The symptoms of a fungal infection in cats are often easy to recognize. Typical symptoms are bald patches in the coat, which are usually roundish and accompanied by scaly or reddened skin. Other symptoms can include itching, inflammation and brittle claws. In severe cases, crusts or suppurations form and some cats show hardly any symptoms, but can be fungal carriers and infect other animals or humans. It is therefore important to pay attention to the slightest changes in coat or behavior.
What symptoms indicate a fungal infection in cats?
Bald, scaly patches of skin, hair loss and itching are clear signs.
What does a fungal infection look like on the skin?
The skin often appears red or scaly and may have small crusts or sores.
Diagnostic procedures at the vet
The vet uses various methods to diagnose a fungal infection. A UV lamp can be used to visualize fungi, which fluoresce under the light. To confirm the diagnosis, a fungal culture is usually taken, in which samples of the coat or skin are examined in the laboratory, and a microscopic examination of the hair roots can also provide evidence of an infection. These procedures are important in order to make an accurate diagnosis and rule out other skin diseases.
How is a fungal infection diagnosed in cats?
The vet examines the skin with a UV lamp and takes samples for further analysis.
Can a vet detect fungal infections under the microscope?
Yes, hair samples can be examined for fungal infestation under the microscope.
Treatment of fungal infections
Medical treatment approaches
Fungal infections in cats are usually treated with antimycotics. These drugs can be administered as tablets, ointments or shampoos. In mild cases, local treatment with ointments or creams is sufficient, while severe infections require systemic therapy, the duration of treatment depends on the severity of the infection and can take several weeks. Regular check-ups with the vet are important to monitor the success of the treatment.
How is a fungal infection treated in cats?
With a combination of antifungals and local treatments such as shampoos.
Which medications or ointments are used for fungal infections?
Antimycotics such as itraconazole or miconazole are frequently used.
How long does the treatment of a fungal infection take?
Treatment can take two to six weeks or longer, depending on the severity.
Hygiene and disinfection
In addition to treating the cat, comprehensive cleaning of the environment is crucial. Fungal spores can survive on textiles, carpets and cat accessories. Use disinfectants that are specifically effective against fungal spores and wash textiles at high temperatures.
Is it necessary to disinfect the cat’s environment?
Yes, thorough disinfection prevents re-infection.
How do you clean the environment after a fungal infection?
Clean surfaces with disinfectants and wash textiles at a temperature of at least 60 degrees.
Home remedies and alternative approaches
Some home remedies such as apple cider vinegar or coconut oil are often mentioned as supportive measures. However, these should never replace medical treatment. Always speak to a vet before trying alternative approaches.
Are there home remedies for fungal infections in cats?
Home remedies such as apple cider vinegar can be used as a supplement, but are no substitute for medication.
Prevention and infection
Preventive measures
To prevent a fungal infection in cats, you should pay attention to good hygiene. Avoid contact with infected animals. Regular brushing and cleaning the environment are important measures. A strong immune system helps the cat to fight off infections.
How can you prevent fungal infections in cats?
Keep the environment clean and make sure your cat’s immune system is strong.
Are there vaccines against fungal infections in cats?
No, there are currently no vaccines against skin fungi in cats.
Risk of infection for other animals and humans
Fungal infections in cats are highly contagious. They can spread to other pets and even to humans. Children and people with a weakened immune system should be particularly careful.
Is a fungal infection in cats contagious?
Yes, fungal infections can easily spread to other animals and humans.
Can I catch a fungal infection from my cat?
Yes, the infection can spread to humans. Good hygiene is important.
Special situations and aftercare
Special risk groups
Young, old or immunocompromised cats are particularly at risk of developing a fungal infection. These animals should be monitored particularly closely and treated at the first sign of infection.
Can young or old cats get fungal infections more easily?
Yes, their immune system is often weaker, which makes them more susceptible.
What to do if the fungal infection does not disappear despite treatment?
Contact your veterinarian to discuss alternative treatment plans.
Aftercare and long-term support
After successful treatment, it is important to continue to monitor the cat. Regular check-ups at the vet will help to prevent a relapse. Ensure a healthy diet and hygienic conditions.
How can you ensure that the fungal infection does not return?
By providing a clean environment and strengthening the cat’s immune system.
Can a fungal infection cause long-term damage?
Usually not, if treated in time. However, severe cases can leave scars.
Fungal infection in cats
Fungal infections in cats are treatable, but require attention and consistency. Early diagnosis, effective treatment and good hygiene are the key to recovery. With the right preventative measures, you can protect your cat from re-infection.